SECTION 206-09: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control
| 2014 Flex Workshop Manual
|
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
| Procedure revision date: 05/02/2013
|
Overview
The ABS and stability control system is comprised of the following subsystems which assist the driver in maintaining control of the vehicle:
The base ABS helps to maintain steering control by preventing the wheels from locking up during hard braking. The base ABS also includes a brake assist function that will provide maximum brake system pressure during a severe braking situation.
The EBD system helps to maintain vehicle control by keeping a balanced braking condition between the front and rear wheels.
The traction control system helps to prevent loss of traction by reducing drive-wheel spin during acceleration.
The trailer sway control system helps maintain vehicle stability while towing a trailer by detecting and aiding in the reduction of conditions that cause trailer sway.
The ESC system helps to prevent skids or lateral slides by activating portions of the base ABS.
The RSC® system helps to prevent excessive vehicle roll by activating portions of the base ABS.
The supplemental braking assist system uses the hydraulic pump motor and HCU to provide additional braking assist in the event of a severe vacuum loss at the brake booster, to maintain the distance gap set by the adaptive cruise control system or to aid in the avoidance of forward collisions.
For information on the Adaptive Cruise Control system, refer to Section 419-03B .
For information on the Collision Avoidance system, refer to Section 419-03C .
System Operation
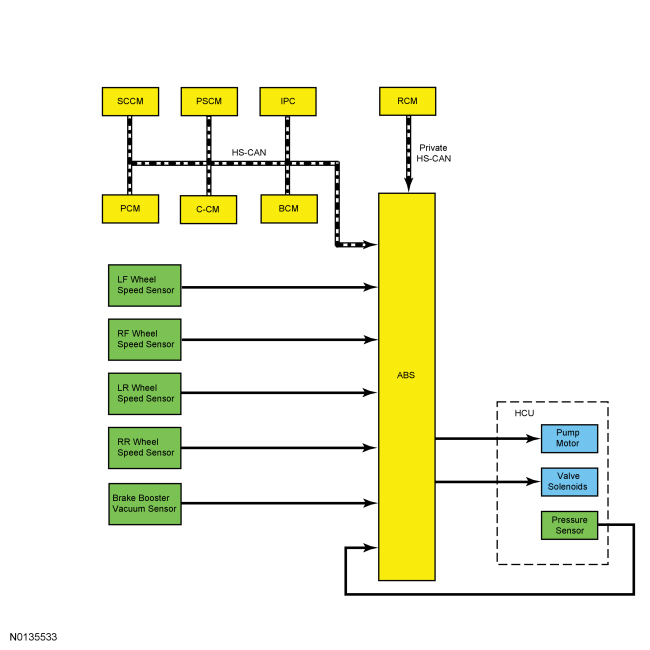
Network Message Chart
ABS Module Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Accelerator pedal position | PCM | The ABS module uses accelerator pedal position information for correct operation of the traction control and ESC systems. |
| Adaptive cruise control brake precharge request | C-CM | The adaptive cruise control system uses the ABS module for braking. This message is used to alert the ABS module that the adaptive cruise control braking event requires a precharge of the hydraulic system. |
| Adaptive cruise control brake request | C-CM | Used to alert the ABS module that the adaptive cruise control system needs to brake. |
| Adaptive cruise control deceleration request | C-CM | Used to alert the ABS module that the adaptive cruise control system needs to decelerate. |
| Adaptive cruise control monitor error | BCM | Used to alert the ABS module that there is an error in the adaptive cruise control system. |
| Brake pedal applied | PCM | Used to inform the ABS module that the driver has pressed the brake pedal. This message is also used by the ABS module to check the brake pressure sensor located inside the HCU . |
| Brake switch on/off | PCM | Used to inform the ABS module that the driver has pressed the brake pedal. This message is also used by the ABS module to check the brake pressure sensor located inside the HCU . |
| Car mode | BCM | The vehicle stability control system reacts differently depending on the current car mode; normal, factory, transport or crash. This message informs the ABS module of the current car mode. |
| Collision mitigation by braking brake precharge request | C-CM | The collision mitigation by braking system uses the ABS module for braking. Used to alert the ABS module that the collision mitigation by braking event requires a precharge of the hydraulic system. |
| Collision mitigation by braking brake request | C-CM | Used to alert the ABS module that the collision mitigation by braking system needs to brake. |
| Collision mitigation by braking deceleration request | C-CM | This message is used to alert the ABS module that the collision mitigation by braking system needs to decelerate. |
| Collision mitigation by braking monitor error | BCM | Used to alert the ABS module that there is an error in the collision mitigation by braking system. |
| Cruise control mode | PCM | Used to inform the ABS module of the current cruise control mode; not active, keeping speed, accelerating, decelerating, resuming high, resuming low, tap up waiting or tap down waiting. |
| Cruise control override | PCM | Used to inform the ABS module that the PCM has denied the driver requested cruise control activation. |
| Cruise control status | PCM | Used to inform the ABS module of the current status of the cruise control system; off, denied, standby or active. |
| Engine off status | PCM | Used to inform the ABS module that the engine is no longer running. |
| Engine RPM | PCM | Used to inform the ABS module of the current engine RPM. The ABS module uses this information for traction control and ESC system operations. |
| Ignition status | BCM | Used to inform the ABS module of the current ignition status; off, accessory, run, start, invalid or unknown. |
| RCM serial number | RCM | The ABS module stores the RCM serial number and verifies the serial number when the vehicle is started or the ignition is set to run or accessory. Over time, the ABS module learns the offset of the sensors inside the RCM . When a new serial number is found, the ABS module resets the offset number learned for ESC operation. |
| Selector lever (PRNDL) status | PCM | This message provides the ABS module with the current transmission gear status. The ESC function does not operate when the transmission is in REVERSE. |
| Steering angle calibration | PSCM (vehicles without active park assist) | This message indicates at what angle the steering wheel is turned. |
| Steering angle calibration | SCCM (vehicles with active park assist) | This message indicates at what angle the steering wheel is turned. |
| Steering angle count | PSCM (vehicles without active park assist) | The ABS module uses this message to determine the validity of the steering angle sensor signal. |
| Steering angle count | SCCM (vehicles with active park assist) | The ABS module uses this message to determine the validity of the steering angle sensor signal. |
| Steering angle initialization | PSCM (vehicles without active park assist) | This message indicates at what angle the steering wheel is turned. |
| Steering angle initialization | SCCM (vehicles with active park assist) | This message indicates at what angle the steering wheel is turned. |
| Traction control on/off | IPC | This message informs the ABS module that the driver has requested the traction control system be disabled or enabled. |
| Transmission shift in progress | PCM | This message is used by the ABS module for traction control performance. |
| Vehicle configuration data_Axle ratio | BCM | This message informs the ABS module of the current vehicle axle ratio. This information allows the ABS module to calculate wheel speed information before sending it out on the HS-CAN . |
| Vehicle configuration data_Collision mitigation by braking | BCM | This message informs the ABS module that the vehicle is equipped with the collision warning system. |
| Vehicle configuration data_Cruise control | BCM | This message informs the ABS module that the vehicle is equipped with cruise control. |
| Vehicle configuration data_Engine fuel capability | BCM | This message informs the ABS module of the current vehicle fuel type, gasoline or diesel. |
| Vehicle configuration data_Forward collision warning | BCM | This message informs the ABS module that the vehicle is equipped with the collision warning system. |
| Vehicle configuration data_Gearbox type | BCM | This message informs the ABS module of the type of transaxle the vehicle is equipped with, manual or automatic transaxle. |
| Vehicle configuration data_Keyless entry and start | BCM | This message informs the ABS module if the vehicle is equipped with IA . |
| Vehicle configuration data_ RCM aux id | BCM
| This message is a redundancy of the RCM serial number message. |
| Vehicle configuration data_Steering wheel location | BCM | This message informs the ABS module of the steering wheel location, LH drive or RH drive. |
| Vehicle configuration data_Tire size | BCM | This message informs the ABS module of the current vehicle tire size. This information allows the ABS module to calculate wheel speed information before sending it out on the HS-CAN . |
| Vehicle configuration data_ VIN number | BCM | This message informs the ABS module of the current VIN . The ABS stores the VIN and will set a DTC if the stored VIN does not match the vehicle configuration data message. |
| Wheel torque data | PCM | Used to inform the ABS module of the current drive wheel torque output in Newton meters. This message is used by the ABS module for traction control and ESC performance. |
Base ABS Function
The ABS module continuously monitors brake pedal input, lateral vehicle motion and the rotational speed of each wheel. The PCM sends the brake pedal switch information to the ABS module over the HS-CAN while the RCM sends lateral acceleration sensor information to the ABS module over a private HS-CAN . Wheel speed information is retrieved by the ABS module using 4 active wheel speed sensors, one for each wheel. When the ABS module detects an impending wheel lock during a braking event, the ABS module modulates brake pressure to the appropriate brake caliper(s) by opening and closing the appropriate solenoid valves inside the HCU while the hydraulic pump motor is activated. Once the affected wheel(s) return to the desired speed, the ABS module returns the solenoid valves in the HCU to their normal position.
The ABS module has 2 self-test options, one is carried out using a scan tool and the other is carried out when the ABS is initialized (ignition ON). During either self test the ABS module carries out a preliminary electrical check of the system sensors and activates the hydraulic pump motor for approximately one-half second. During this time, a buzzing or humming noise may be heard and a vibration may be felt in the brake pedal and is a normal condition. During the module initialized self test, the pump motor check is carried out at approximately 10 km/h (6.2 mph). Any malfunction detected in the system causes the module to set a DTC, disable the ABS function and send a message over the HS-CAN to the IPC to illuminate the ABS warning indicator. However, the base hydraulic power-assist braking system will function normally.
Electronic Brake Distribution (EBD)
On initial application of the brake pedal, full pressure is applied to the rear brakes. The ABS module then uses wheel speed sensor inputs to calculate an estimated rate of deceleration. Once vehicle deceleration exceeds a predetermined threshold, the ABS module commands the HCU to close the appropriate isolation valves to hold the rear brake pressure constant while allowing the front brake pressure to build. This creates a balanced braking condition between the front and rear wheels. As the vehicle decelerates, the valves are opened to increase the rear brake pressure in proportion to the front brake pressure. A slight bump sensation may be felt in the brake pedal when EBD is active. If the ABS is disabled due to DTCs being present in the ABS module, EBD continues to function unless the DTCs are for wheel speed sensors or the HCU /solenoid valves. When EBD is disabled, the ABS warning indicator, the red brake warning indicator and sliding car icon illuminate.
Traction Control
The ABS module continuously monitors and compares the rotational speed of the drive wheels in relation to the non-driven wheels. When the drive wheels begin to spin faster than the non-driven wheels, the ABS module modulates brake pressure to the appropriate brake caliper(s) by opening and closing the appropriate solenoid valves inside the HCU while the hydraulic pump motor is activated. At the same time, the ABS module calculates how much engine torque reduction is required to eliminate the wheel slip and sends this torque reduction message to the PCM over the HS-CAN . The ABS module also sends a traction event message to the IPC over the HS-CAN . When the PCM receives the torque reduction message, it adjusts engine timing and decreases fuel injector pulses to reduce the engine torque to the requested level. When the IPC receives traction event message, it flashes the sliding car icon.
Once the driven wheel speed returns to the desired speed, the ABS module returns the solenoid valves in the HCU to their normal position, deactivates the hydraulic pump motor and stops sending the traction event and torque reduction messages. The PCM returns engine timing and fuel injectors to normal operation and the IPC extinguishes the sliding car icon. After the vehicle speed exceeds 100 km/h (62.1 mph), traction control is accomplished only through the PCM torque control.
The traction control system can be disabled by the driver through the menu in the message center by changing the TRACTION CNTRL setting in the message center from ON to OFF. This is independent of the ABS and ESC functions, which cannot be disabled by the driver. When the driver disables the traction control function through the message center, the IPC communicates traction control system status to the ABS module over the HS-CAN and illuminates the sliding car OFF icon. The ABS module takes no further action in regards to traction control until the driver activates the function or until the ignition is cycled from OFF to ON.
The ABS module disables the traction control function if there are any wheel speed sensor or solenoid valve DTCs present in the ABS module. The traction control function is also disabled if there is a communication error between the ABS module and the PCM. When the traction control function is disabled, the ABS module sends a message to the IPC over the HS-CAN to illuminate the sliding car OFF icon.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
The ABS module continuously monitors the vehicle motion relative to the intended course. This is done by using sensors to compare the steering wheel input and the yaw rate sensor input with that of the actual vehicle motion. The SCCM (vehicles with active park assist) or PSCM (vehicles without active park assist) sends the steering wheel angle and rate of change information to the ABS module over the HS-CAN while the RCM sends yaw rate sensor information to the ABS module over a private HS-CAN . If the ABS module determines from the inputs that the vehicle is unable to travel in the intended direction, the ABS module modulates brake pressure to the appropriate brake caliper(s) by opening and closing the appropriate solenoid valves inside the HCU while the hydraulic pump motor is activated. At the same time, the ABS module calculates how much engine torque reduction is required to eliminate the wheel slip and sends this torque reduction message to the PCM over the HS-CAN . The ABS module also sends a traction event message to the IPC over the HS-CAN . When the PCM receives the torque reduction message, it adjusts engine timing and decreases fuel injector pulses to reduce the engine torque to the requested level. When the IPC receives traction event message, it flashes the sliding car icon.
Once the vehicle instability has been corrected, the ABS module returns the solenoid valves in the HCU to their normal position, deactivates the hydraulic pump motor and stops sending the traction event and torque reduction messages. The PCM returns engine timing and fuel injectors to normal operation and the IPC extinguishes the sliding car icon.
The ESC function does not operate with the transmission in REVERSE. The ABS module disables the ESC function if there are any wheel speed sensor, stability sensor or steering angle sensor DTCs present in the ABS module. Also, if there is a communication error between the ABS module and the PSCM , the SCCM or the RCM the ESC function is disabled. When the ESC function is disabled, the ABS module sends a message to the IPC over the HS-CAN to illuminate the sliding car icon.
Roll Stability Control (RSC®)
The ABS module continuously monitors the vehicle motion relative to the intended course. This is done by using sensors to compare the steering wheel input and the roll rate sensor input with that of the actual vehicle motion. The SCCM (vehicles with active park assist) or PSCM (vehicles without active park assist) sends the steering wheel angle and rate of change information to the ABS module over the HS-CAN while the RCM sends yaw rate sensor information to the ABS module over a private HS-CAN . If the ABS module determines from the inputs that the vehicle is becoming unstable, the ABS module modulates brake pressure to the appropriate brake caliper(s) by opening and closing the appropriate solenoid valves inside the HCU while the hydraulic pump motor is activated. At the same time, the ABS module calculates how much engine torque reduction is required to eliminate the wheel slip and sends this torque reduction message to the PCM over the HS-CAN . The ABS module also sends a traction event message to the IPC over the HS-CAN . When the PCM receives the torque reduction message, it adjusts engine timing and decreases fuel injector pulses to reduce the engine torque to the requested level. When the IPC receives traction event message, it flashes the sliding car icon.
Once the vehicle instability has been corrected, the ABS module returns the solenoid valves in the HCU to their normal position, deactivates the hydraulic pump motor and stops sending the traction event and torque reduction messages. The PCM returns engine timing and fuel injectors to normal operation and the IPC extinguishes the sliding car icon.
The RSC® function does not operate with the transmission in REVERSE. The ABS module disables the RSC® function if there are any wheel speed sensor, stability sensor or steering angle sensor DTCs present in the ABS module. Also, if there is a communication error between the ABS module and the PSCM , the SCCM or the RCM the RSC® function is disabled. When the RSC® function is disabled, the ABS module sends a message to the IPC over the HS-CAN to illuminate the sliding car icon.
MyKey® Interaction
Through the MyKey® feature, the traction control function of the stability control system can be configured to be always on or to allow the driver to select the traction control function on or off.
When the traction control function is configured to be always on and a MyKey® restricted key is in use, the IPC will ignore any requests made by the driver to disable the traction control function and will not send any traction control disable messages to the ABS module. Refer to the Owner's Literature.
Stability/Traction Control Indicator (Sliding Car Icon)
Refer to Section 413-01 .
Stability/Traction Control Disabled Indicator (Sliding Car OFF Icon)
Refer to Section 413-01 .
Trailer Sway Control
Trailer sway is the undesirable yaw force a trailer can apply to the towing vehicle. Trailer sway control is a unique function of the vehicle dynamic system that uses steering wheel angle information from the SCCM (vehicles with active park assist) or from the PSCM (vehicles without active park assist) and the yaw information from the RCM to determine if a trailer sway event is taking place. If it is determined that an event is taking place, the ABS module modulates brake pressure to the appropriate brake caliper(s) by opening and closing the appropriate solenoid valves inside the HCU while the hydraulic pump motor is activated. At the same time, the ABS module calculates how much engine torque reduction is required to eliminate the trailer sway and sends this torque reduction message to the PCM over the HS-CAN . The ABS module also sends a trailer sway event message to the IPC over the HS-CAN . When the PCM receives the torque reduction message, it adjusts engine timing and decreases fuel injector pulses to reduce the engine torque to the requested level. When the IPC receives trailer sway event message, it flashes the sliding car icon and displays TRAILER SWAY, REDUCE SPEED in the message center.
Once the trailer sway has been corrected, the ABS module returns the solenoid valves in the HCU to their normal position, deactivates the hydraulic pump motor and stops sending the trailer sway event and torque reduction messages. The PCM returns engine timing and fuel injectors to normal operation and the IPC extinguishes the sliding car icon.
Trailer sway control only activates when vehicle speed is greater than 65 km/h (40.4 mph). Any malfunction that disables the RSC® function of the vehicle dynamic system also disables trailer sway control. Trailer sway control can also be disabled by the driver through the menu in the message center. Regardless of the chosen state (enabled or disabled) set by the driver, trailer sway control is enabled at each ignition key cycle.
Supplemental Braking Assist
The ABS module utilizes the HCU and hydraulic pump motor to aid in bringing the vehicle to a safe, controlled stop in the event of severe vacuum loss at the brake booster. The ABS module continually monitors the vacuum in the brake booster through the use of a vacuum sensor. When the vacuum sensor indicates vacuum is below a predetermined level, a DTC is set in the ABS module. The ABS module sends a message to the IPC over the HS-CAN to illuminate the red brake warning indicator. If a low vacuum condition occurs during a braking event or if the driver attempts to stop the vehicle with a low vacuum condition in the brake booster, the ABS module activates the hydraulic pump motor in the HCU to assist with vehicle braking.
On vehicles equipped with adaptive cruise control, the C-CM monitors the area forward of the vehicle. When an object enters this area and closes the distance gap set by the driver, the C-CM sends a deceleration request to the ABS module over the HS-CAN (either an adaptive cruise control deceleration request or a collision avoidance deceleration request). When the deceleration request message is received, the ABS module activates the hydraulic pump motor and solenoid valves in the HCU to slow the vehicle down to maintain the distance gap set by the driver. Once the distance gap set by the driver is achieved, the C-CM stops sending the deceleration request message and the ABS module deactivates the hydraulic pump motor and solenoid valves in the HCU . If the C-CM determines that the amount of braking provided by the ABS module is insufficient, the C-CM sends a forward collision avoidance braking request message to the ABS module and warns the driver, both audibly and visually, through the use of the HUD . After receiving the braking request message, the ABS module waits for brake pedal input and at that time applies maximum braking assist using the hydraulic pump motor and the HCU . For additional information on the adaptive cruise control system, refer to Section 419-03B . For additional information on the collision avoidance system, refer to Section 419-03C .
Component Description
ABS Module
The ABS module is attached directly to the HCU and is the ECU for all of the ABS and stability control systems. The module monitors all sensor inputs and all HS-CAN messages that relate to ABS and stability control and then directly controls the solenoid valves and the hydraulic pump motor.
The ABS module is available separately for service, however, the module is serviced with the HCU in the event that a new HCU is required. When a new ABS module is installed, whether with a new HCU or not, the module must be programmed with the vehicle information. For additional information on module programming, refer to Section 418-01 .
Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
The HCU contains the solenoid valves, the hydraulic pump motor and the pressure sensor used by the ABS module for the ABS and stability control systems. The ABS module and the HCU are attached directly together. The ABS module is available separately for service, however, the module is serviced with the HCU in the event that a new HCU is required.
Wheel Speed Sensor
Both front wheel speed sensors are active (magneto resistive) sensors that operate on the Hall-effect principle to generate a square wave signal that is proportional to the rotational speed of the wheel. Because these are active sensors, receiving voltage from the ABS module and then sending a varying voltage back to the ABS module, they are able to detect much lower rotational speeds than passive (magnetic inductive) sensors. Each wheel speed sensor is connected to the ABS module by 2 circuits. One circuit provides voltage for sensor operation and the other circuit provides sensor input to the ABS module.
Both rear wheel speed sensors are active, bi-directional sensors. Each of the 2 sensors contain 2 sensing elements mounted side-by-side. Because the 2 sensing elements are mounted next to each other the 2 voltage signals are slightly out of phase, which causes one element to generate a voltage signal before the other element. This allows the ABS module to not only determine wheel speed, but also wheel direction for active park assist.
Wheel Speed Sensor Magnetic Strips
The wheel speed sensor magnetic strips are made up of many magnets arranged in a circle around one side of the wheel bearing in alternating poles, so as the bearing rotates the wheel speed sensor is exposed to alternating north-south magnetic fields. The magnetic strip is located on the side of the wheel bearing facing the vehicle and is part of the wheel bearing and, as such, is serviced with the bearing.
Stability Control Sensors
The stability control sensors for the vehicle dynamic system consist of the yaw rate sensor, lateral accelerometer and longitudinal accelerometer. The sensors are housed in the RCM which sends sensor information to the ABS module over a private HS-CAN . If any of the sensors are inoperative, a new RCM must be installed.
Lateral acceleration has 2 forms. The first is the centrifugal acceleration that is generated when the vehicle travels around in a circle. The second is the acceleration due to gravity. On level ground there is no lateral acceleration due to gravity. However, if the vehicle is parked sideways on a bank or incline, the sensor measures some lateral acceleration due to gravity, even though the vehicle is not moving.
Steering Wheel Rotation Sensor
On vehicles not equipped with active park assist, the steering wheel rotation speed and direction of travel is determined by the PSCM and is sent to the ABS module over the HS-CAN .
On vehicles equipped with active park assist, the steering wheel rotation sensor directly measures the steering wheel rotation speed and direction of rotation. The sensor is mounted on the SCCM and the information is sent to the ABS module over the HS-CAN .
Brake Booster Vacuum Sensor
The brake booster vacuum sensor is a piezoelectric device used by the ABS module to monitor the vacuum in the brake booster. The sensor is hardwired to the ABS module by 3 circuits. One circuit is for the 5 volt sensor supply, one circuit is for sensor ground and one circuit is for sensor output. The sensor output ranges from 0.2 volt to 4.9 volts, depending on the amount of vacuum in the booster. The sensor is located on the front of the brake booster can be serviced separately from the brake booster.