SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transmission — 6F50/6F55
| 2014 Flex Workshop Manual
|
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
| Procedure revision date: 05/02/2013
|
Component Location
The solenoid body contains 5 shift solenoids, 1 TCC solenoid and 1 LPC solenoid.
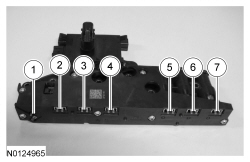
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | SSE |
| 2 | SSD |
| 3 | SSA |
| 4 | TCC |
| 5 | SSB |
| 6 | SSC |
| 7 | LPC |
System Operation
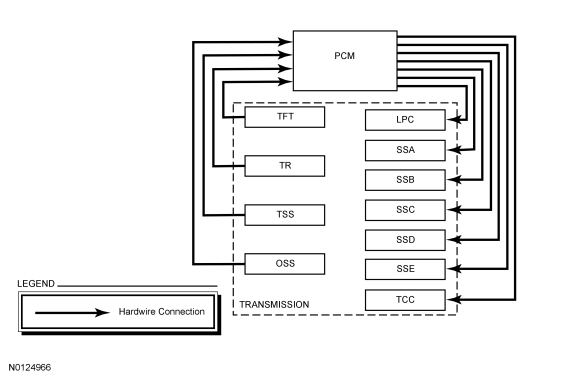
The PCM and its input/output network controls the following operations:
The transmission control strategy is separate from the engine control strategy in the PCM, although some of the input signals are shared. When determining the best operating strategy for transmission operation, the PCM uses input information from engine and driver related sensors and switches.
In addition, the PCM receives input signals from transmission related sensors and switches. The PCM uses these signals when determining transmission operating strategy.
Using all of these input signals, the PCM can determine when the time and conditions are right for a shift or when to apply or release the TCC . It also determines the best line pressure to optimize shift engagement feel. To accomplish this, the PCM uses output solenoids to control transmission operation.
Network Message Chart
Communication Message Chart
| Message | Originating Module | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Speed | PCM | Directly affects shift scheduling, TCC control, line pressure and transmission diagnostics. Indirectly affects shift pressure control. |
| Engine torque estimate | PCM | Directly affects shift pressure control, TCC control and transmission diagnostics. Indirectly affects shift scheduling and TCC scheduling. |
| APP | PCM | Directly affects shift scheduling, TCC scheduling and transmission diagnostics. Indirectly affects TCC control and shift control. |
| Commanded engine torque | PCM | Directly affects shift scheduling, TCC scheduling and transmission diagnostics. Indirectly affects shift control. |
| BPP | PCM | Directly affects shift scheduling and TCC scheduling |
Component Description
Sensors and Switches
The PCM controls the electronic functions of this transmission. The PCM receives input signals from engine and transmission sensors and uses these inputs to control line pressure, shift time, TCC and shift solenoids.
| Item | Description |
| TFT Sensor | This sensor is located in the transmission solenoid body. It is a temperature-sensitive device called a thermistor. The resistance value of the
TFT
sensor will vary with temperature change. The PCM monitors the voltage across the
TFT
sensor to determine the temperature of the transmission fluid.
The PCM uses this initial signal to determine whether a cold start shift schedule is necessary. The cold start shift schedule allows delayed shifts when the transmission fluid is cold to help warm the transmission fluid. The PCM also inhibits TCC operation at low transmission fluid temperatures and adjusts line pressure for temperature. |
| TR Sensor | The TR sensor has a 6-pin electrical connector. The TR sensor is located on the inside of the transmission at the manual control lever. The TR sensor sends a signal to the PCM to start the vehicle in PARK and NEUTRAL. The TR sensor opens/closes a set of 4 switches that are monitored by the PCM to determine the position of the manual control lever. |
| TSS Sensor | This TSS sensor is a Hall-effect pickup that sends a signal to the PCM that indicates transmission turbine shaft input speed. The TSS information is compared to engine rpm to determine TCC performance. TSS is also compared to OSS to determine shift quality and clutch performance. |
| OSS Sensor | The OSS sensor is a Hall-effect pickup, located on the transfer shaft drive gear, that sends a signal to the PCM to indicate transmission output speed. The OSS is used for shift scheduling. OSS is also compared to TSS to determine shift quality and clutch performance. |
Solenoid Body
The solenoid body contains 7 solenoids: 5 shift solenoids ( SSA , SSB , SSC , SSD and SSE ), 1 TCC solenoid and 1 LPC solenoid. The TFT sensor is located in the solenoid body. The solenoid body is serviced as an assembly.
The solenoid body has a unique strategy data file that must be downloaded to the PCM. There is a 7-digit solenoid body identification and a 13-digit solenoid body strategy for each solenoid body. When a new solenoid body or transmission is installed, the scan tool must be used to get the solenoid body strategy data file and download it into the PCM.
If the PCM is replaced and the PCM data cannot be inhaled or exhaled, the solenoid body identification and solenoid body strategy must be downloaded into the PCM.
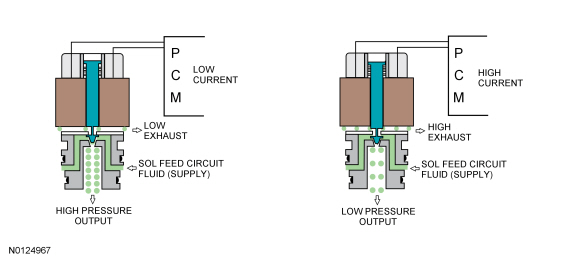
This transmission uses 3 types of solenoids: On/Off, normally low and normally high. On/Off solenoids open or close hydraulic passages based on the voltage signal it receives. Normally low solenoids provide hydraulic pressure proportional to supplied current. A normally low solenoid will not provide pressure without current, while it will supply high pressure with high current. Normally high solenoids provide pressure inversely proportional to supplied current. Normally high solenoids provide full output of pressure with no current and very low pressure with high current.
ON/OFF Solenoids
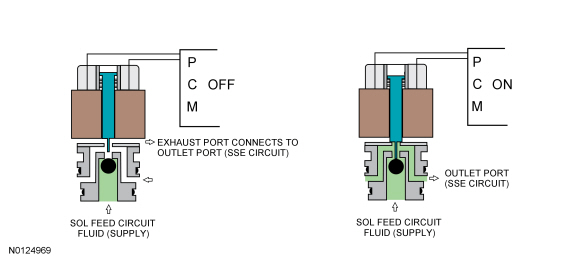
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| SSE | Normally closed solenoid that blocks SOL FEED pressure from the SSE circuit. When energized, pressure from the SSE circuit positions the multiplex shift valve to direct CBLR/C456 SUPPLY pressure to the low reverse clutch. |
Normally Low Solenoids
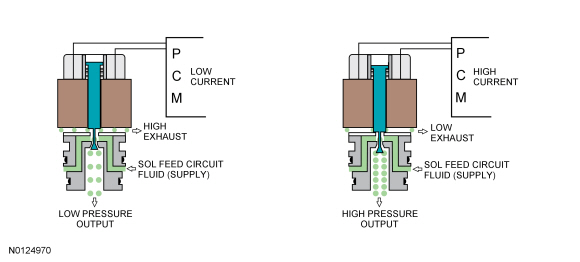
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| SSA | SSA blocks SOL FEED pressure from the SSA SIG circuit when low current is supplied. When energized, SSA SIG pressure positions the CB1234 clutch regulator and boost valves to direct CB1234 SUP pressure to apply the forward clutch. |
| SSC | SSC blocks SOL FEED pressure to the SSC SIG circuit when low current is supplied. When energized, SSC SIG pressure positions the CB26 clutch regulator valve to direct CB26FD/CB1234FD pressure to apply the intermediate clutch. |
| TCC | The TCC solenoid is used in the transmission control system to control the application, modulation and release of the torque converter clutch. The TCC solenoid blocks SOL FEED pressure to the TCC SOL SIG circuit when low current is supplied. When energized, TCC SOL SIG pressure positions the TCC reg apply and control valves to direct REG APPLY pressure to apply the torque converter. |
Normally High Solenoids
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| SSB | SSB feeds SOL FEED pressure to the SSB SIG circuit to position the direct (3,5,R) clutch regulator and boost valves to apply the direct (3,5,R) clutch. When energized, SSB blocks SSB SIG to position the direct clutch (3,5,R) regulator and boost valves to release the direct (3,5,R) clutch. |
| SSD | SSD feeds SOL FEED pressure to the SSD SIG circuit to position the CBLR/C456 regulator and boost valves to apply either the low/reverse clutch or the overdrive (4,5,6) clutch. When energized, SSD blocks SSD SIG to position the CBLR/C456 regulator and boost valves to release either the low/reverse clutch or the overdrive (4,5,6) clutch. |
| LPC | The LPC solenoid is used to apply resistive force to the main regulator valve to adjust line pressure. Line pressure is inversely proportional to the current supplied to the LPC solenoid. As current decreases, line pressure increases. |