SECTION 413-01: Instrumentation, Message Center, and Warning Chimes
| 2014 Flex Workshop Manual
|
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
| Procedure revision date: 05/02/2013
|
Overview
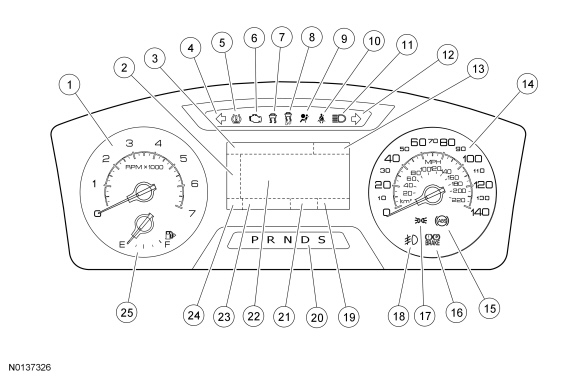
| Item | Part Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | — | Tachometer |
| 2 | — | Main menu navigation |
| 3 | — | Main menu text display |
| 4 | — | LH turn indicator |
| 5 | — | TPMS warning indicator |
| 6 | — | MIL |
| 7 | — | Stability-traction control indicator (sliding car icon) |
| 8 | — | Stability-traction control disabled indicator (sliding car OFF icon) |
| 9 | — | Air bag warning indicator |
| 10 | — | Safety belt warning indicator |
| 11 | — | High beam indicator |
| 12 | — | RH turn indicator |
| 13 | — | Cruise control display area |
| 14 | — | Speedometer |
| 15 | — | ABS warning indicator |
| 16 | — | Brake warning indicator |
| 17 | — | Lights on indicator |
| 18 | — | Fog lamp indicator |
| 19 | — | Odometer |
| 20 | — | PRNDL display |
| 21 | — | Compass display |
| 22 | — | Message center display area |
| 23 | — | Message center indicator display area |
| 24 | — | Select shift display area |
| 25 | — | Fuel gauge |
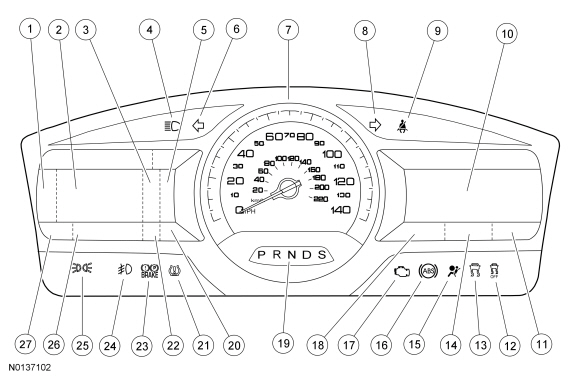
| Item | Part Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | — | Menu navigation icon |
| 2 | — | LH message center display (also displays the analog style tachometer and select shift display [if equipped] and AWD gauge [if equipped]) |
| 3 | — | Adaptive cruise control display (if equipped) |
| 4 | — | High beam indicator |
| 5 | — | Fuel gauge, fuel gauge/tachometer or fuel gauge/temperature gauge display |
| 6 | — | LH turn indicator |
| 7 | — | Speedometer |
| 8 | — | RH turn indicator |
| 9 | — | Safety belt warning indicator |
| 10 | — | RH multimedia display area |
| 11 | — | Clock display |
| 12 | — | Stability-traction control disabled indicator (sliding car OFF icon) |
| 13 | — | Stability-traction control indicator (sliding car icon) |
| 14 | — | Compass display |
| 15 | — | Air bag warning indicator |
| 16 | — | ABS warning indicator |
| 17 | — | MIL |
| 18 | — | Outside air temperature display |
| 19 | — | PRNDL display |
| 20 | — | Select shift display area |
| 21 | — | TPMS warning indicator |
| 22 | — | Cruise control message center indicator (fixed) |
| 23 | — | Brake warning indicator |
| 24 | — | Fog lamp indicator |
| 25 | — | Lights on indicator |
| 26 | — | Message center indicator display area (rotating) |
| 27 | — | Odometer |
The base IPC is available with a single LCD screen. The optional IPC is available with dual RH and LH LCD screens. The single display screen and the LH display screen contain the message center information. The RH display screen displays multimedia information (audio, phone and navigation), as well as items such as vehicle direction, outside air temperature and time.
Refer to the appropriate section in Group 415 for the procedure.
Informational Indicators/Warning Indicators
Informational indicators provide information to the driver of conditions that exist in the vehicle. Warning indicators provide information to the driver of conditions that could potentially cause personal injury or alter vehicle performance.
Message Center Indicators
Message center indicators illuminate in the message center and replace the typical informational or warning indicator using the same iconic representation. When multiple warnings exist, the message center indicators cycle through each display until the condition has been corrected unless the message center indicator is in a fixed position. The message center indicators include:
Networked Message Inputs
Module messaging has increased over time and has become the standard for sending and receiving information required to operate the IPC . The majority of the inputs required to operate the IPC are received over the CAN .
Hardwired Inputs
The IPC requires hardwired inputs from components that are not on the HS-CAN or MS-CAN . These components are required for specific IPC functions or gateway requirements. Refer to Gateway Function in Section 419-10 .
The hardwired inputs are provided by:
System Operation
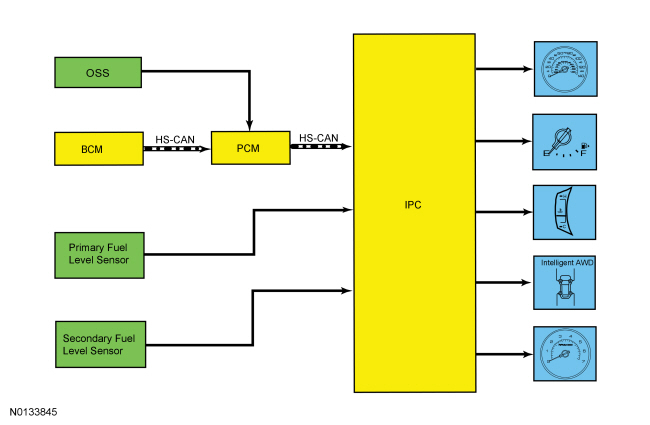
Network Message Chart — Gauges
Module Network Input Messages — IPC
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| AWD lock torque actual | PCM | Input used for the AWD gauge display. |
| Engine coolant temperature | PCM | Engine temperature data used for temperature gauge indication. |
| Engine coolant temperature fault reporting | PCM | Input used to determine the quality of the engine temperature data input for the temperature gauge indication. |
| Engine overheat failsafe mode | PCM | Input used to send the temperature gauge to full hot when in failsafe cooling mode. |
| Engine rpm | PCM | Engine speed data used for tachometer indication and the low oil pressure message center warning indicator. |
| Ignition status | BCM | Ignition RUN, START and accessory states required for the IPC operating modes and fault reporting. |
| Vehicle speed | PCM | Vehicle speed data used for speedometer indication.
Input used for the AWD gauge display. |
| Vehicle speed fault reporting | PCM | Input used to determines the quality of the vehicle speed data input for the speedometer indication. |
| Wheel torque data | PCM | Input used for the AWD gauge display. |
System Diagram — Indicators
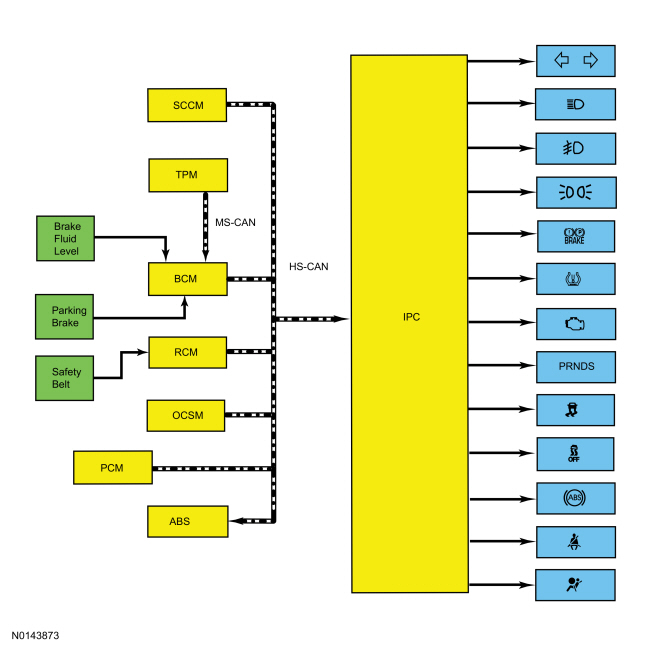
Network Message Chart — Indicators
Module Network Input Messages — IPC
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Air bag indicator request | RCM | Restraints indicator lamp request used to control the air bag warning indicator. |
| ABS warning indicator request | ABS module | Input required for the ABS warning indicator. |
| Brake warning indicator request | BCM | Input from the BCM required for the brake fluid level and parking brake components of the brake warning indicator operation. |
| Brake (red) warning indicator request | ABS module | Input required from the ABS module for the ABS and EBD components of the brake warning indicator. |
| Engine MIL request | PCM | Input used for the MIL . |
| Fog lamp indicator request | BCM | Input required for the fog lamps indicator. |
| Headlamp high beam indicator request | BCM | Input required for the high beam indicator. |
| Ignition status | BCM | Ignition RUN, START and accessory states required for the IPC operating modes and fault reporting. |
| Parklamp status | BCM | Input used to trigger the lights on indicator. |
| Safety belt indicator request | RCM | Input used to control the safety belt warning indicator. |
| Stability-traction control indicator | ABS module | Input required for the stability/traction control indicator (sliding car icon). |
| Stability-traction control disabled (OFF) indicator | ABS module | Input required for the stability/traction control disabled indicator (sliding car OFF icon). |
| Transmission gear display actual | PCM | Transmission range input used for the PRNDL display. |
| Transmission gear display status | PCM | Transmission range input used for the PRNDL display. |
| Transmission shift mode | PCM | Input used to control the grade assist indicator. |
| Tire pressure warning indicator | BCM | Input required for the IPC to illuminate or flash the TPMS warning indicator. |
| Turn indicator command | BCM | RH and LH turn signal/hazard inputs required for the RH and LH turn/hazard indicator. |
Networked Input Messages and Default States
The IPC uses input messages from other modules to control the gauges, informational indicators, and warning indicators over the communication networks. If a required message is missing or invalid for less than 5 seconds, the gauge or indicator that requires the message remains at the last commanded state based upon the last message received. For example, if the stability-traction control status message is missing for less than 5 seconds and the stability-traction control indicator (sliding car icon) was on, the indicator remains on until the next message is received. If the message remains missing or invalid for more than 5 seconds, the IPC sets a U-code DTC and the IPC output becomes a default action for the indicator or gauge. Each indicator or gauge utilizes a different default strategy depending on the nature of the indication. Refer to the diagnostic overview descriptions located before each individual pinpoint test for further description of the default action specific to each indicator or gauge. If the missing messaged input to the IPC returns at any time, normal function of the gauge or indicator resumes.
NOTE: Whenever a network message is suspected as missing and confirmed by a missing message DTC (U-code), it is important to look for other symptoms that may also be present in the IPC and throughout the vehicle. Once a DTC sets in the IPC , it may be helpful to review the complete message list. Refer to Section 418-00 , CAN Multiplex Messages Description and Operation, to determine which other modules also rely on the same message and run the self-test for those modules. If the message is missing from other modules, the same DTC may also be set in those modules. Confirmation of missing messages common to multiple modules may indicate the originating module is the source of the concern or the communication network may be faulted.
It is very important to understand:
Configuration
The IPC contains items that are configurable. Configurable items include customer preference items, which can also be set with a scan tool. The remaining configurable items can only be set by the PMI procedure by uploading/downloading existing configuration or by using As-Built data. Refer to the scan tool instructions. The configurable IPC items are:
| Customer Preference | As-Built Parameter | State Description |
|---|---|---|
| — | 2WD / 4WD / AWD |
|
| — | ABS |
|
| — | Adaptive cruise control |
|
| — | Adaptive headlamps |
|
| — | Advance traction control function |
|
| — | AWD gauge |
|
| — | Auto high beams |
|
| — | Autolamp delay |
|
| — | Autolock control |
|
| — | Auto unlock control |
|
| — | Active park assist |
|
| — | Average fuel economy metric type |
|
| — | Back up chime (Japan only) |
|
| — | Belt-Minder® |
|
| — | Camera active guide 1 |
|
| — | Camera delay |
|
| — | Camera parkaid |
|
| — | Camera zoom |
|
| — | Chime generator |
|
| — | Compass LIN based |
|
| — | Compass GPS based |
|
| — | Continuously controlled dampening |
|
| — | Courtesy wipers |
|
| — | Cross traffic alert |
|
| — | Cruise control menu |
|
| — | Do not disturb |
|
| — | Doors |
|
| — | Driver alert |
|
| — | DSP present |
|
| — | Easy entry-easy exit |
|
| — | Emergency assist |
|
| — | Engine hours |
|
| — | EPAS |
|
| — | Flex fuel |
|
| — | Forward collision warning |
|
| — | Front fog |
|
| — | Gallon type |
|
| — | Gear select/select shift |
|
| — | Global window open |
|
| — | Global window closed |
|
| — | Idle hours |
|
| — | Key-in-ignition chime |
|
| — | Lane assist |
|
| — | Lane departure warning OFF telltale |
|
| — | Language |
|
| — | Language bundle - country code |
|
| — | Multiple chimes |
|
| — | MyKey® |
|
| — | MyKey® speed limiter |
|
| — | MyKey® volume |
|
| — | Neutral tow |
|
| — | Number of fuel senders |
|
| — | Number of fuel tanks |
|
| — | Oil minder |
|
| — | Oil pressure input type | CAN |
| — | Outside air temperature |
|
| — | Overspeed chime |
|
| — | Park aid front |
|
| — | Park aid rear |
|
| — | Passive entry/passive start |
|
| — | Police auxiliary |
|
| — | Power liftgate |
|
| — | PTY type |
|
| — | Rain sensing wipers |
|
| — | Rear camera |
|
| — | Rear fog |
|
| — | Remote start |
|
| — | Remote start-climate |
|
| — | Remote start-driver |
|
| — | Remote start-passenger |
|
| — | Remote start-rear defrost |
|
| — | Remote start-steering wheel |
|
| — | Reverse gear wiper |
|
| — | Right hand screen — phone |
|
| — | Right hand screen — navigation |
|
| — | Right hand screen — climate |
|
| — | Right hand screen — entertainment Sirius |
|
| — | Right hand screen — entertainment digital audio band (Europe only) |
|
| — | Right hand screen — entertainment compact disc |
|
| — | RSC® chime |
|
| — | Side detection |
|
| — | Side marker lamp telltale |
|
| — | Speedometer calibration |
|
| — | Tank size A |
|
| — | Tire kit |
|
| — | Traction control/interactive vehicle dynamics/ RSC® |
|
| — | Trailer sway |
|
| — | Transmission type |
|
| — | TPMS configuration |
|
| — | Turn-by-turn navigation |
|
| — | Two stage unlocking |
|
| — | Welcome and farewell |
|
| — | Welcome ignition behavior |
|
Dealer Test Mode
To enter the IPC dealer mode, begin with the ignition in the OFF mode. Press and hold the LH steering wheel switch OK button. Place the ignition in the ON mode and hold the button until the dealer test mode popup window appears, usually within 3 to 5 seconds. Press the up or down arrow buttons to navigate through each of the display windows. To exit the IPC self-test mode, press and hold the OK button for 3-5 seconds or place the ignition in the OFF mode. The dealer test mode displays multiple items in a viewing window on the LH side of the IPC . Each button press advances the viewing window to the next set of items.
NOTE: The table below lists the displays as they appear when navigating using the down arrow button.
| Button Press | Viewing Window Content | Information Display | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Part Number Information (base IPC ) | PartNo: xxxx-xx
Core: xxxx-xx Cal#: xxxx-xx ECU S/W: xxxx-xx | Displays the alphanumeric prefix and suffix of the IPC part number. |
| 1 | Part Number Information (optional IPC ) | xxxx-xx
xxxx-xx xxxx-xx xxxx-xx | Displays the alphanumeric prefix and suffix of the IPC part number. |
| 2 | Fuel Level (Dual Fuel Sender) | Inst Fuel1: xxx
FLPM1: xxxx.x FLPM: xxxx.x | Displays the primary (fuel pump assembly) fuel level and average fuel level. |
| 3 | Fuel Level (Dual Fuel Sender) | Inst Fuel2: xxx
FLPM2: xxxx.x FLPM: xxxx.x | Displays the secondary (fuel level sensor) fuel level and average fuel level. |
Transport Mode
The vehicle is placed in a transport mode at the completion of production to reduce the drain on the battery. Various systems may be altered in how they operate or are disabled when in the transport mode. The vehicle automatically reverts to normal operation after 201 km (125 miles). To disable or turn off the transport mode, carry out the following within 10 seconds:
Factory Mode
During vehicle assembly, the vehicle defaults to factory mode. Factory mode sets the function timers such as PRNDL display to further reduce the drain on the battery during assembly. The vehicle is placed into transport mode at the end of vehicle assembly. The vehicle remains in factory mode for 60 ignition cycles or until it is manually changed to transport mode.
Gateway Function
The IPC acts as a gateway module by receiving information in one format and transmitting it to the audio and multimedia modules using another format. This enables network communication between modules that do not communicate using the same network ( I-CAN or HS-CAN ).
MyKey®
The MyKey® feature allows the customer to program a restricted driving mode that is tied to one or more keys known as a MyKey® key. When a MyKey® programmed key is in use, the IPC provides the following functions:
When an administrator key is in use, the IPC provides the following functions:
For information on the MyKey® features, refer to the Owner's Literature.
Prove-Out
The IPC and other vehicle modules carry out a display prove-out to verify all module controlled warning/indicator lamps and monitored systems are functioning correctly within the IPC . The IPC and other modules, such as the RCM , provide a timed prove out while other indicators illuminate until engine start up. When the ignition is cycled to on with the engine off, the indicators illuminate to prove-out according to the following table:
| Indicator | Indicator Type | Prove-Out Duration |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Warning | 3 seconds |
| Air bag | Warning | 6 seconds |
| Brake | Warning | 3 seconds |
| Fog lamp | Informational | None |
| High beam | Informational | None |
| Lights on | Informational | None |
| MIL | Warning | Engine startup |
| Safety belt | Warning | 70 seconds if the safety belt is unbuckled, turns off when the safety belt is buckled |
| Stability-traction control (sliding car icon) | Warning | 3 seconds |
| Stability-traction control disabled (sliding car OFF icon) | Informational | 3 seconds |
| TPMS | Warning | 3 seconds |
| RH/LH turn | Informational | None |
Startup-Shutdown
The IPC provides a startup/shutdown sequence also known as a welcome/farewell strategy. When the vehicle receives a RKE request or a door ajar (open) message, the IPC illuminates the gauge trim rings and pointers. When the ignition is placed in the ACC mode, all cluster backlighting, gauges and indicators are turned off. When the ignition is placed into the RUN or START mode, the IPC begins a prove-out stage. During the prove-out stage, the IPC illuminates all LED indicators for a predetermined time and provides message center information. For the shutdown, the IPC reverses the startup process.
Transport Mode
During vehicle build, some vehicle modules ( IPC , BCM and RFR module [if equipped]) are set in factory mode. While in the factory mode the IPC displays FACTORY MODE CONTACT DEALER in the message center. If the vehicle is set in factory mode, the system does not automatically exit the mode and must be manually set to either the transport or normal operation mode. When the vehicle build is complete, the vehicle is set to transport mode. While in transport mode, the IPC displays TRANSPORT MODE CONTACT DEALER in the message center. Transport mode is used to reduce the drain on the battery during longer periods where the vehicle is not used. Various systems may be altered or are disabled when in the transport mode. The vehicle automatically reverts to normal operation mode after being driven 201 km (125 mi). To disable or turn off the transport mode, refer to Section 419-10 .
Fuel Gauge
The IPC sends a reference voltage to the fuel level senders. As the fuel level changes, a separate float on each sender actuates the variable resistor fuel level senders, raising or lowering the fuel level signal voltages. The IPC monitors the changes in voltage from both senders and commands the fuel gauge with a corresponding movement of the pointer.
Depending on which operating mode the fuel gauge is in after a fuel fill up, the time for the fuel gauge to move from empty (E) to full (F) ranges from 2 seconds to 55 minutes.
The IPC uses 4 different operating modes to calculate the fuel level:
The default fuel gauge mode is called the anti-slosh mode. To prevent fuel gauge changes from fuel slosh (gauge instability due to changes in fuel sensor readings caused by fuel moving around in the tank), the fuel gauge takes approximately 55 minutes to go from empty (E) to full (F).
The key OFF fueling mode (2 seconds to read empty [E] to full [F]) requires 3 conditions be met:
If these conditions are not met, the fuel gauge stays in the anti-slosh mode, which results in a slow to read full (F) event.
The key ON fueling mode (approximately 60 seconds to read empty [E] to full [F]) requires the following conditions be met:
In key ON fueling mode, a 30-second timer activates after the transmission is put into the PARK (P) or NEUTRAL (N) position. When the 30-second time has elapsed and at least 9% of the vehicle's fuel capacity has been added, the fuel gauge response time is 60 seconds to read from empty (E) to full (F). When the transmission is shifted out of PARK (P) or NEUTRAL (N), the fuel gauge strategy reverts to the anti-slosh mode. The key ON fueling mode prevents slow to read full events from happening if the customer refuels the vehicle with the ignition in the RUN mode.
Recovery mode is incorporated into the IPC strategy to recover from a missing fuel level input after a refueling event. Missing fuel level inputs result from intermittent opens in the fuel sensor or its circuits. Recovery mode (empty [E] to full [F] approximately 20 minutes) is initiated when the following 2 conditions are met:
Temperature Gauge
The temperature gauge is located in the LCD display area and is a graphical image as opposed to the more traditionally recognized analog gauge. The base IPC uses a thermometer style image that moves upward as the engine temperature increases, changing color as the temperature reaches predetermined ranges. When the temperature is in the cold band, the thermometer color is blue. When the temperature is in the normal band, the thermometer color is gray, and when the temperature is in the hot band, the thermometer color is red. The optional IPC uses a graphical gauge image with a single bar set horizontally across the gauge that moves vertically from bottom to top as the engine temperature increases. The PCM uses the CHT sensor to measure the engine temperature. The IPC uses the engine coolant temperature message from the PCM to control the temperature gauge indication.
Speedometer
The PCM calculates the vehicle speed from the transmission OSS sensor input and from the tire size and axle ratio configuration in the PCM VID block. The PCM provides the IPC with a vehicle speed data message to command the speedometer pointer.
The IPC provides a tolerance which allows the gauge to display between 3% lower and 7% higher than the actual vehicle speed. This means that with an actual vehicle speed of 96.6 kmh (60 mph), the speedometer may indicate between 93.7 kmh (58.2 mph) and 103.3 kmh (64.2 mph), which is normal.
Odometer
The IPC receives the odometer count message from the PCM. The IPC monitors the odometer count input from the PCM and commands the odometer with a digital display in the message center.
Tachometer
The PCM uses the CKP sensor to measure the engine rpm. The IPC uses the engine Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) data message from the PCM to control the tachometer. The base and optional IPC tachometers appear differently but function the same. The base IPC uses an analog gauge. The optional IPC uses a digital display that provides a 6,000 rpm bar graph or a 7,000 rpm simulated analog gauge display depending on the selected display mode.
AWD Gauge
The AWD gauge displays the level of power applied to each wheel. The IPC uses the following inputs to determine the AWD gauge display:
As power is applied to the wheels, the area directly in front of each displayed wheel begin to fill in. The lowest power displayed is the closest to the wheel. As the amount of power sent to the wheels increases, the area fills in either forward (front wheels) or rearward (rear wheels) of the wheels.
Brake Warning Indicator
The IPC uses 3 basic messaged inputs to control the brake warning indicator. The first 2 messages are the parking brake position switch and the brake fluid level switch sent from the BCM . The third is the for EBD and low brake booster vacuum or vacuum sensor fault messages sent from the ABS module.
The parking brake position switch is hardwired to the BCM through a single signal circuit, while using a separate ground to control the input. The brake fluid level switch is hardwired to the BCM through separate signal and return circuits to control the input.
The BCM provides a reference voltage to both the parking brake position switch and the brake fluid level switch. When the parking brake is applied, the parking brake position switch closes to ground, pulling the reference voltage on the parking brake signal circuit low. When a low brake fluid level condition exists, the brake fluid level switch closes to ground pulling the reference voltage on the brake fluid level signal circuit low. When the brake fluid level switch is disconnected, the reference voltage on the brake fluid level signal circuit is sent high. When the BCM detects the parking brake is applied, a low brake fluid level condition exists or the brake fluid level switch is disconnected, the BCM sends the IPC a brake warning indicator request.
When the ABS module detects a base brake system concern or other ABS related concerns that affect the EBD function or brake booster vacuum, the ABS module sends a brake (red) warning indicator request to the IPC to illuminate the brake warning indicator and the ABS warning indicator.
ABS Warning Indicator
The IPC uses the ABS warning indicator request from the ABS module to control the ABS warning indicator. If a fault condition exists in the ABS, the ABS module sends the IPC the ABS warning indicator request to either flash or illuminate the ABS warning indicator.
Stability-Traction Control Indicator (Sliding Car Icon)
The IPC uses a traction control indicator request message from the ABS module to control the stability-traction control indicator (sliding car icon). The stability-traction control indicator (sliding car icon) flashes when the vehicle stability-traction control is in active mode or is being controlled by the ABS module. The stability-traction control indicator (sliding car icon) illuminates continuously if a fault condition exists in the stability-traction control system. The IPC monitors the traction control indicator request message from the ABS module and either flashes the stability-traction control indicator (sliding car icon) or illuminates it steady depending on the condition.
Stability-Traction Control Disabled Indicator (Sliding Car OFF Icon)
The stability-traction control is configured on/off through the message center. When the stability-traction control is configured on or off, the IPC sends a message to the ABS module indicating the stability-traction control system has been enabled or disabled by the driver. The ABS module either enables or disables the stability-traction control system, and sends a traction control disabled (OFF) indicator request back to the IPC to illuminate or turn off the stability-traction control disabled indicator (sliding car OFF icon) based upon the system state. The stability/traction control system defaults back on or enabled once the ignition is cycled off then back on again.
When a MyKey® programmed key is in use and the AdvanceTrac® on feature is configured always on, the traction control system cannot be disabled and the stability-traction control disabled indicator (sliding car OFF icon) does not illuminate when the traction control is disabled. The stability-traction control indicator still functions normally to indicate a stability-traction control system fault and a stability-traction control active event.
Safety Belt Warning Indicator
The RCM monitors the safety belt position through the safety belt buckle switch. The RCM sends a safety belt indicator request to the IPC to illuminate the safety belt warning indicator.
Air Bag Warning Indicator
The IPC receives the air bag warning indicator lamp request from the RCM . If a SRS concern is detected, the RCM sets a DTC and sends an air bag indicator lamp request to the IPC to illuminate the air bag warning indicator.
LH-RH Turn Signal Indicator
When the multifunction switch is in the LH or RH turn position or if the hazard switch is on, a turn indicator command message is sent to the IPC from the BCM . Upon receipt of the applicable turn signal on/off request, the IPC flashes the turn signal indicator on and off.
High Beam Indicator
When the high beams are turned on, the BCM sends a headlamp high beam indicator request to the IPC to illuminate the high beam indicator.
TPMS Warning Indicator
The IPC receives TPMS data from the BCM . The BCM receives the tire pressure status message from the TPM module. If the BCM determines the tire pressure has exceeded the low tire pressure limits, a tire pressure status message is sent to the IPC to illuminate the TPMS warning indicator. If a TPMS fault condition exists, the BCM sends the tire pressure status message to the IPC . The IPC flashes the TPMS warning indicator for 75 seconds, then illuminates the indicator continuously.
When the TPMS is in tire train mode, the BCM sends a message to the IPC to flash the TPMS warning indicator.
Lights On Indicator
When the parking lamps are turned on either through the exterior lighting functions or the illuminated entry feature, the BCM sends the position light indication message to the IPC to illuminate the lights on indicator.
MIL
The MIL is controlled by the IPC using an engine MIL request from the PCM.
PRNDL/Select Shift Indicator
The IPC receives the selector lever (PRNDL) status message from the PCM. The IPC also uses a park detect switch (part of the selector lever) input to signal the IPC that the shift lever is fully seated in the PARK (P) position. The IPC compares the park detect switch input with the selector lever (PRNDL) status message sent from the PCM and illuminates the appropriate gear position in the PRNDL indicator.
The IPC provides a battery reference voltage to the brake shift interlock. When the selector lever is in PARK (P), the brake shift indicator routes the reference voltage to ground, pulling the circuit low to the IPC . When the selector lever is moved out of PARK (P), the brake shift interlock opens the ground sending the reference voltage high.
The select shift display area indicates to the driver which gear is currently selected when the transmission is in the select shift mode. When the transmission is in select shift manual mode, the gear number is displayed in the select shift display area preceded by the letter M (example: M1, M2, M3 etc).
Component Description
Brake Fluid Level Switch
The brake fluid level switch is a reed-type switch that is mounted through the master cylinder reservoir. The reservoir uses a magnet incorporated into the float. The brake fluid level switch is hardwired to the BCM through separate signal and return circuits and is grounded to a body ground through a separate circuit. The BCM provides a reference voltage to the brake fluid level switch. When the brake fluid level is low, the float drops allowing the magnet to close the reed switch, pulling the reference voltage low. When the brake fluid level is high, the float lifts, releasing the switch contacts and removing the ground to the BCM .
Fuel Level Sender
The fuel level sender is mounted to the fuel pump assembly or the fuel level sensor. The fuel level sender is a dual sweep potentiometer style resistor connected to a float mechanism. The dual sweep design provides a second resistance measurement that reduces the intermittent loss of data due to corrosion between the resistor wires and the sweep arm. As the fuel level changes, the float rises or falls with the fuel level moving the sweep arm across the resistor wires. This movement either increases or decreases the resistance through the unit. The fuel level sensor resistance ranges from 180 ohms ± 4 ohms at empty (E) to 10 ohms ± 2 ohms at full (F). When the fuel level is low, the fuel level sensor resistance is high. When the fuel level is high, the fuel level sensor resistance is low.
Both the fuel pump assembly and fuel level sensor are hardwired to the IPC through separate signal and return circuits. The fuel level return circuits are grounded internally in the IPC . The IPC provides a reference voltage on the fuel level signal circuit. As the fuel level changes, the change in resistance raises or lowers the fuel level signal voltage depending on the resistance of the fuel level sender.
Parking Brake Position Switch
The parking brake position switch is hardwired to the BCM through a signal and return circuit. The BCM provides a reference voltage on the signal circuit. The return circuit is grounded internally in the BCM . When the parking brake is not applied, the parking brake position switch is open. When the parking brake is applied, the parking brake position switch closes, pulling the reference voltage low.
Park Position Detect Switch
The park position detect switch is hardwired to the IPC through a single signal circuit. The park position detect switch is hardwired to a separate ground circuit. The IPC provides a reference voltage to the park position detect switch. When the selector lever is in PARK (P), the park position detect switch routes the reference voltage to ground, pulling the circuit low to the IPC . When the selector lever is moved out of PARK (P), the park position detect switch opens to ground sending the reference voltage high.
IPC
The IPC provides the driver with a system status and alerts the driver when certain conditions exist in the vehicle. The IPC requires PMI when the IPC is replaced.