
POM6411 or equivalent
NUD105-R025D or equivalent

162-00036 or equivalent
SGT27000
SECTION 414-00: Charging System
| 2014 Flex Workshop Manual
|
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
| Procedure revision date: 05/02/2013
|
 | Backprobe Pins
POM6411 or equivalent |
 | Flex Probe Kit
NUD105-R025D or equivalent |
 | GR 1 190 V3.0 Intelligent Diagnostic Charger
162-00036 or equivalent |
 | Test Light SGT27000 or equivalent 250-350 mA incandescent bulb test lamp
SGT27000 |
DTC Charts
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. REFER to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
NOTE: The BCM utilizes a 5-character DTC followed by a 2-character failure-type code. The failure-type code provides information about specific fault conditions such as opens or shorts to ground. CMDTCs have an additional 2-character DTC status code suffix to assist in determining DTC history.
PCM DTC Chart
| DTC | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| P0562 | System Voltage Low | GO to Pinpoint Test B . |
| P0563 | System Voltage High | GO to Pinpoint Test A . |
| P0620 | Generator Control Circuit | GO to Pinpoint Test C . |
| P0625 | Generator Field Terminal Circuit Low | GO to Pinpoint Test D . |
| P0626 | Generator Field Terminal Circuit High | GO to Pinpoint Test D . |
| P065B | Generator Control Circuit Range/Performance | If combined with P0625, GO to Pinpoint Test d . If P0625 is not present, GO to Pinpoint Test E . |
| P0A5A | Generator Current Sensor Circuit Range/Performance | GO to Pinpoint Test H . |
| P0A5B | Generator Current Sensor Circuit Low | GO to Pinpoint Test H . |
| P0A5C | Generator Current Sensor Circuit High | GO to Pinpoint Test H . |
| P1397 | System Voltage Out Of Self-Test Range | If combined with P0562,
GO to Pinpoint Test B
.
If combined with P0563, GO to Pinpoint Test A . |
| All other DTCs | — | REFER to the PCM DTC Chart in Section 303-14 . If directed to this section from another section, GO to Symptom Chart in this section. |
BCM DTC Chart
| DTC | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| U1007:31 | Lost Communication With Battery Monitoring Sensor "A": No Signal | GO to Pinpoint Test I . |
| U3003:16 | Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Below Threshold | GO to Pinpoint Test B . |
| U3003:17 | Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Above Threshold | GO to Pinpoint Test A . |
| All other DTCs | — | REFER to Section 419-10 . |
Symptom Chart
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. REFER to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
Pinpoint Tests
Pinpoint Test A: System Voltage High
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. Refer to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 12 , Charging System for schematic and connector information.
With the engine running, the charging system supplies voltage to the battery and the vehicle electrical system through the high current BJB and battery B+ cable. The voltage that is supplied to the vehicle electrical system is used for the operation of the various vehicle systems and modules. Many modules monitor this voltage and if it rises above or below their calibrated setpoints, a DTC sets.
Before diagnosing or repairing the charging system inspect the following items:
NOTE: DTC P1397 can be set if the vehicle has been recently jump started, the battery has been recently charged or the battery has been discharged. The battery may become discharged due to excessive load(s) on the charging system from aftermarket accessories or if vehicle accessories have been operating for an extended period of time without the engine running.
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| System Voltage High | If the module detects a voltage from the charging system higher than 15.2 volts, this DTC sets. This DTC does not set in the PCM unless the vehicle speed is above 8 km/h (5 mph). |
| System Voltage Out of Self-Test Range | If the voltage rises above or drops below the calibrated set point, the PCM sets this DTC. This DTC may also be set if the vehicle has been recently jump started or has had a discharged battery. |
| Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Above Threshold | Sets in the BCM when the BCM detects that battery voltage has gone above 15.9 volts from the voltage supply circuit. |
NOTE: Make sure battery voltage is greater than 12.2 volts prior to and during this pinpoint test.
NOTE: Do not have a battery charger attached during vehicle testing.
| Test Step | Result / Action to Take | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 CHECK BATTERY CONDITION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to A2 . No INSTALL a new battery. REFER to Section 414-01 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A2 RETRIEVE DTCs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
For DTC P0620, GO to Pinpoint Test C . For DTCs P0625 and P0626, GO to Pinpoint Test D . For DTC P065B, GO to Pinpoint Test E . No GO to A3 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A3 MONITOR THE GENERATOR VOLTAGE DESIRED (GENVDSD) PID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to A4 . No GO to A12 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A4 COMPARE THE GENERATOR VOLTAGE DESIRED (GENVDSD) PID WITH BATTERY VOLTAGE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. No GO to A5 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A5 MEASURE THE "A" SENSE VOLTAGE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to A6 . No VERIFY high current BJB fuse 58 (5A) is OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the possible causes of the circuit short. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A6 "A" SENSE CIRCUIT LOAD TEST | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTICE: The following step uses a test light to simulate normal circuit loads. Use only the test light recommended in the Special Tools table at the beginning of this section. To avoid connector terminal damage, use the Flex Probe Kit for the test light probe connection to the vehicle. Do not use the test light probe directly on any connector. NOTE: This step puts a load on the "A" sense circuit. If there are corroded or loose connections, loading the circuit may help show the fault. A 250-350 mA incandescent 12-volt test lamp is required for this step. This circuit cannot be loaded correctly using an LED-style test lamp.
 | Yes
GO to A7 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A7 CHECK THE VOLTAGE DROP IN THE VEHICLE GROUNDS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to A8 . No INSPECT and REPAIR the engine ground, generator ground or the battery ground for corrosion. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A8 CHECK THE GENERATOR OUTPUT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . No GO to A9 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A9 MONITOR THE GENERATOR COMMAND (GENCMD), GENERATOR MONITOR (GENMON) AND GENERATOR VOLTAGE DESIRED (GENVDSD) PIDs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to A10 . No GO to A12 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A10 COMPARE THE SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VPWR) PID TO BATTERY VOLTAGE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . No GO to A11 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A11 CHECK PCM SUPPLY VOLTAGE CIRCUITS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
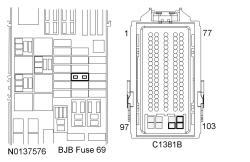 | Yes
GO to A12 . No REPAIR the affected circuit(s). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A12 CHECK FOR CORRECT PCM OPERATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
CHECK OASIS for any applicable TSBs . If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no TSBs address this concern, INSTALL a new PCM. REFER to Section 303-14 . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by module connections. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Pinpoint Test B: System Voltage Low or Battery is Discharged
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. Refer to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 12 , Charging System for schematic and connector information.
With the engine running, the charging system supplies voltage to the battery and the vehicle electrical system through the battery B+ cable. The PCM monitors this voltage through the battery positive post through the high current BJB . If voltage drops 1.5 volts or more below the generator voltage desired, this DTC sets after 30 seconds.
Before diagnosing or repairing the charging system inspect the following items:
NOTE: DTC P0562 or P1397 can be set if the vehicle has been recently jump started, the battery has been recently charged or the battery has been discharged. The battery may become discharged due to excessive load(s) on the charging system from aftermarket accessories or if vehicle accessories have been operating for an extended period of time without the engine running.
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| System Voltage Low | If the PCM detects voltage from the charging system that is 1.5 volts lower than the generator voltage desired, this DTC sets. |
| System Voltage Out of Self-Test Range | If the voltage rises above or drops below the calibrated set point, the PCM sets this DTC. This DTC may also be set if the vehicle has been recently jump started or has had a discharged battery. |
| Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Below Threshold | Sets in the BCM when the BCM detects that battery voltage has dropped below 9 volts from the voltage supply circuit. |
NOTE: Make sure battery voltage is greater than 12.2 volts prior to and during this pinpoint test.
NOTE: Do not have a battery charger attached during vehicle testing.
| Test Step | Result / Action to Take |
|---|---|
| B1 CHECK BATTERY CONDITION | |
| Yes
GO to B2 . No INSTALL a new battery. REFER to Section 414-01 . |
| B2 RETRIEVE PCM DTCs | |
| Yes
For DTC P0620, GO to Pinpoint Test C . For DTCs P0625 and P0626, GO to Pinpoint Test D . For DTC P065B, GO to Pinpoint Test E . No GO to B3 . |
| B3 CHECK THE GENERATOR CONNECTIONS | |
| Yes
GO to B4 . No VERIFY the fusible links are OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the possible causes of the circuit short. |
| B4 CHECK THE VOLTAGE DROP IN THE B+ CIRCUIT | |
| Yes
GO to B5 . No INSPECT and REPAIR any corrosion in the generator B+ circuit or positive battery cable connections. |
| B5 CHECK THE VOLTAGE DROP IN THE VEHICLE GROUNDS | |
| Yes
GO to B6 . No INSPECT and REPAIR the engine ground, generator ground or the battery ground for corrosion. |
| B6 MONITOR THE GENERATOR VOLTAGE DESIRED (GENVDSD) PID WHILE COMMANDED | |
| Yes
GO to B7 . No INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . |
| B7 COMPARE THE SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VPWR) PID TO BATTERY VOLTAGE | |
| Yes
GO to B8 . No REPAIR high resistance or loose connections in the affected PCM power circuit(s). |
| B8 CHECK PCM GROUND FOR HIGH RESISTANCE | |
| Yes
GO to B9 . No REPAIR the affected PCM ground circuits. |
| B9 MONITOR THE SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VPWR) PID | |
| Yes
The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. INSPECT and REPAIR any connector or pin issues found. If no connector or pin issues are found, CARRY OUT the battery drain test. REFER to Section 414-01 . No GO to B10 . |
| B10 CHECK FOR CORRECT PCM OPERATION | |
| Yes
CHECK OASIS for any applicable TSBs . If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no TSBs address this concern, INSTALL a new PCM. REFER to Section 303-14 . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by module connections. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Pinpoint Test C: DTC P0620
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. Refer to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 12 , Charging System for schematic and connector information.
The PCM monitors the generator output via the generator monitor (GENMON) circuit. The PCM uses the generator command (GENCOM) circuit to command the generator to either increase or decrease output. If the GENCOM circuit (generator control circuit) or the "A" sense circuit are open or shorted to ground, the PCM will not be able to control the generator output. When the engine speed is greater than 2,000 rpm, the generator defaults to a steady voltage output of 13.5 volts and the PCM sends a request to the IPC to illuminate the charging system warning indicator. A GENCOM circuit fault can be confirmed by viewing the PCM PID generator command line fault (GENCMD_LF) (YES status indicator fault).
Before diagnosing or repairing the charging system inspect the following items:
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Generator Control Circuit | The PCM sets this DTC if the GENCOM circuit or "A" sense circuit are open or shorted to ground. |
NOTE: Make sure battery voltage is greater than 12.2 volts prior to and during this pinpoint test.
NOTE: Do not have a battery charger attached during vehicle testing.
| Test Step | Result / Action to Take | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 CHECK THE BATTERY CONDITION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to C2 . No INSTALL a new battery. REFER to Section 414-01 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C2 CHECK THE GENERATOR CONNECTIONS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to C3 . No VERIFY the fusible links are OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the possible causes of the circuit short. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C3 CHECK THE VOLTAGE DROP IN THE B+ CIRCUIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to C4 . No INSPECT and REPAIR any corrosion in the generator B+ circuit or positive battery cable connections. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C4 "A" SENSE CIRCUIT LOAD TEST | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTICE: The following step uses a test light to simulate normal circuit loads. Use only the test light recommended in the Special Tools table at the beginning of this section. To avoid connector terminal damage, use the Flex Probe Kit for the test light probe connection to the vehicle. Do not use the test light probe directly on any connector. NOTE: This step puts a load on the "A" sense circuit. If there are corroded or loose connections, loading the circuit may help show the fault. A 250-350 mA incandescent 12-volt test lamp is required for this step. This circuit will not be loaded properly using an LED-style test lamp.
 | Yes
GO to C5 . No VERIFY high current BJB fuse 58 (5A) is OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the possible causes of the circuit short. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C5 CHECK THE GENERATOR COMMAND CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO VOLTAGE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
REPAIR the circuit. No GO to C6 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C6 CHECK THE GENERATOR COMMAND CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO GROUND | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to C7 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C7 CHECK THE GENERATOR COMMAND CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
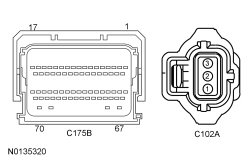
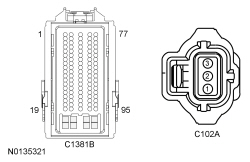 | Yes
GO to C8 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C8 COMPARE THE GENERATOR MONITOR (GENMON) AND GENERATOR COMMAND (GENCMD) PIDs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
REMOVE the fused jumper wire. INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . No REMOVE the fused jumper wire. GO to C9 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C9 CHECK FOR CORRECT PCM OPERATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
CHECK OASIS for any applicable TSBs . If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no TSBs address this concern, INSTALL a new PCM. REFER to Section 303-14 . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by module connections. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Pinpoint Test D: DTC P0625 or P0626
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. Refer to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 12 , Charging System for schematic and connector information.
The PCM monitors the generator output via the generator monitor (GENMON) circuit (generator field terminal circuit). If the PCM cannot read the GENMON circuit due to an open or short to ground, when the engine speed is greater than 2,000 rpm, the generator defaults to a steady voltage of 13.5 volts and the PCM sends a request to the IPC to illuminate the charging system warning indicator. A GENMON duty cycle of 3% or less indicates a short to ground fault is present and results in DTC P0625 setting in the PCM. A GENMON duty cycle of 98% or more indicates an open or short to voltage fault is present and results in DTC P0626 setting in the PCM.
Before diagnosing or repairing the charging system inspect the following items:
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Generator Field Terminal Circuit Low | The PCM sets this DTC if the GENMON circuit is shorted to ground, the "A" sense circuit is open or the B+ circuit is open. This DTC also sets by a faulted PCM or generator. |
| Generator Field Terminal Circuit High | The PCM sets this DTC if the GENMON circuit is open or shorted to power. This DTC can also be set by a faulted PCM or generator. |
NOTE: Make sure battery voltage is greater than 12.2 volts prior to and during this pinpoint test.
NOTE: Do not have a battery charger attached during vehicle testing.
| Test Step | Result / Action to Take | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 CHECK THE BATTERY CONDITION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to D2 . No INSTALL a new battery. REFER to Section 414-01 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D2 CHECK THE GENERATOR CONNECTIONS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to D3 . No VERIFY the fusible links are OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the possible causes of the circuit short. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D3 CHECK THE VOLTAGE DROP IN THE B+ CIRCUIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
For DTC P0625, GO to D4 . For DTC P0626, GO to D5 . No INSPECT and REPAIR any corrosion in the generator B+ circuit or positive battery cable connections. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D4 "A" SENSE CIRCUIT LOAD TEST | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTICE: The following step uses a test light to simulate normal circuit loads. Use only the test light recommended in the Special Tools table at the beginning of this section. To avoid connector terminal damage, use the Flex Probe Kit for the test light probe connection to the vehicle. Do not use the test light probe directly on any connector. NOTE: This step puts a load on the "A" sense circuit. If there are corroded or loose connections, loading the circuit may help show the fault. A 250-350 mA incandescent 12-volt test lamp is required for this step. This circuit will not be loaded properly using an LED-style test lamp.
 | Yes
GO to D5 . No VERIFY high current BJB fuse 58 (5A) is OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the possible causes of the circuit short. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D5 CHECK THE GENERATOR MONITOR CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO VOLTAGE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
REPAIR the circuit. No GO to D6 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D6 CHECK THE GENERATOR MONITOR CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO GROUND | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to D7 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D7 CHECK THE GENERATOR MONITOR CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||

 | Yes
GO to D8 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D8 CHECK THE GENERATOR B+ INTERNAL RESISTANCE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to D9 . No INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D9 CHECK THE RESISTANCE OF THE VOLTAGE REGULATOR INTERNAL CIRCUITS TO GROUND | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
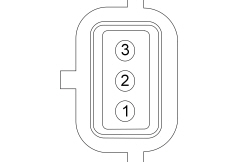 | Yes
GO to D10 . No INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D10 COMPARE THE GENERATOR MONITOR (GENMON) AND GENERATOR COMMAND (GENCMD) PIDs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
REMOVE the fused jumper wire. INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . No REMOVE the fused jumper wire. GO to D11 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D11 CHECK FOR CORRECT PCM OPERATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
CHECK OASIS for any applicable TSBs . If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no TSBs address this concern, INSTALL a new PCM. REFER to Section 303-14 . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by module connections. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Pinpoint Test E: DTC P065B
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. Refer to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 12 , Charging System for schematic and connector information.
With the engine running, the PCM monitors and expects to receive a valid generator monitor (GENMON) signal with a duty cycle greater than 5% and less than 98%. The PCM also monitors the state of the generator command (GENCMD) signal line to make sure it is not stuck high or stuck low. A DTC sets if the GENMON or GENCMD signal fluctuates between out-of-valid range, stuck high, stuck low, or some combination and normal. When the engine speed is greater than 2,000 rpm, the generator defaults to a steady voltage of 13.5 volts and the PCM sends a request to the IPC to illuminate the charging system warning indicator lamp.
Before diagnosing or repairing the charging system inspect the following items:
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Generator Control Circuit Range/Performance | The PCM sets this DTC if the input frequency was continuously less than 80 Hz or more than 200 Hz. Additionally, if the signal shows a faulted condition that is happening in a fluctuating manner, the PCM tracks the fluctuations between faulted and normal conditions. This DTC can also set if the fluctuations occur frequently within a short amount of time. |
NOTE: Make sure battery voltage is greater than 12.2 volts prior to carrying out this pinpoint test.
NOTE: Do not have a battery charger attached during vehicle testing.
| Test Step | Result / Action to Take | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 CHECK THE BATTERY CONDITION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to E2 . No INSTALL a new battery. REFER Section 414-01 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E2 CHECK THE GENERATOR CONNECTIONS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to E3 . No VERIFY the fusible links are OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the possible causes of the circuit short. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E3 "A" SENSE CIRCUIT LOAD TEST | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTICE: The following step uses a test light to simulate normal circuit loads. Use only the test light recommended in the Special Tools table at the beginning of this section. To avoid connector terminal damage, use the Flex Probe Kit for the test light probe connection to the vehicle. Do not use the test light probe directly on any connector. NOTE: This step puts a load on the "A" sense circuit. If there are corroded or loose connections, loading the circuit may help show the fault. A 250-350 mA incandescent 12-volt test lamp is required for this step. This circuit will not be loaded properly using an LED-style test lamp.
 | Yes
GO to E4 . No VERIFY high current BJB fuse 58 (5A) is OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the possible causes of the circuit short. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E4 CHECK THE GENERATOR MONITOR FREQUENCY (GENMON_HZ) PID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to E8 . No GO to E5 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E5 CHECK THE GENERATOR MONITOR FREQUENCY (GENMON_HZ) PID WITH GENERATOR DISCONNECTED | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to E7 . No GO to E6 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E6 CHECK GENERATOR MONITOR CIRCUIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTICE: This pinpoint test step directs testing circuits using a back-probe method. Use the special back-probe tool specified in the tool list in this section. Do not force test leads or other probes into connectors. Use care to avoid connector terminal damage while making sure that good electrical contact is made with the circuit or terminal. Failure to follow these instructions may cause damage to wiring, terminals, or connectors and subsequent electrical faults.
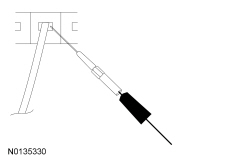
 | Yes
INSPECT the harness for wire to wire shorts or insulation chaffing, mis-pinned connectors and correct wire colors and REPAIR the circuit as needed. No GO to E9 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E7 MONITOR THE GENERATOR MONITOR FREQUENCY (GENMON_HZ) PID WHILE ACTIVATING THE GENERATOR VOLTAGE DESIRED (GENVDSD) PID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . No GO to E9 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E8 CHECK THE GENERATOR COMMAND LINE FAULT (GENCMD_LF) PID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by an intermittently loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E9 CHECK FOR CORRECT PCM OPERATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
CHECK OASIS for any applicable TSBs . If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no TSBs address this concern, INSTALL a new PCM. REFER to Section 303-14 . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by module connections. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Pinpoint Test F: The Generator is Noisy
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. Refer to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 12 , Charging System for schematic and connector information.
The generator is belt-driven by the engine accessory drive system. There are several sources of generator noise which include bearing noise, electrical fault noise, generator or belt pulley misalignment. A generator with certain types of diode or stator failures may also produce an audible noise.
Before diagnosing or repairing the charging system inspect the following items:
| Test Step | Result / Action to Take |
|---|---|
| F1 CHECK FOR ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT NOISE AND LOOSE MOUNTING BRACKETS | |
| Yes
GO to F2 . No REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 303-05 . |
| F2 CHECK THE GENERATOR MOUNTING | |
| Yes
GO to F3 . No REPAIR as necessary. |
| F3 CHECK THE GENERATOR FOR NOISE | |
| Yes
INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . No REFER to Section 303-00 , to diagnose the source of the engine noise. |
Pinpoint Test G: Radio Interference
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. Refer to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 12 , Charging System for schematic and connector information.
The generator radio suppression equipment reduces interference transmitted through the speakers by the vehicle electrical system.
Before diagnosing or repairing the charging system inspect the following items:
NOTE: If the OEM ACM has been replaced with an aftermarket unit, the vehicle may not pass this test. Return the vehicle to OEM condition before following this pinpoint test.
NOTE: If the engine is operated at greater than 2,000 rpm momentarily, the generator self-excites. Make sure when the generator is disconnected the engine rpm stays below 2,000 rpm. If it exceeds 2,000 rpm, turn the ignition to the OFF position and start the test over again.
NOTE: Inspect for any aftermarket accessories that have been added to the vehicle. Check the wiring for these accessories and be sure they have not been attached to the generator circuits and are positioned away from the generator wiring.
| Test Step | Result / Action to Take |
|---|---|
| G1 VERIFY THE GENERATOR IS THE SOURCE OF THE RADIO INTERFERENCE | |
| Yes
Refer to the appropriate section in Group 415 for the procedure. No INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Generator . TEST the system for normal operation. |
Pinpoint Test H: DTC P0A5A, P0A5B, P0A5C
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. Refer to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 13 , Power Distribution/BCM for schematic and connector information.
The generator current sensor is a Hall-effect sensor attached to the generator B+ cable. It is supplied a 5 volt reference and ground from the PCM. The PCM reads the generator current sensor feedback voltage to determine how much current is flowing through the generator B+ cable.
Before diagnosing or repairing the charging system inspect the following items:
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Generator Current Sensor Circuit Range/Performance | The PCM does not detect current through the generator current sensor and there are no generator current sensor circuit DTCs set. |
| Generator Current Sensor Circuit Low | The PCM senses lower than expected voltage on the generator current sensor feedback circuit, indicating an open or a short directly to ground. |
| Generator Current Sensor Circuit High | The PCM senses higher than expected voltage on the generator current sensor feedback circuit, indicating a short directly to voltage. |
| Test Step | Result / Action to Take | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 CHECK THE PCM DTCs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to H2 . No For DTC P0A5B, GO to H3 . For DTC P0A5C, GO to H7 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H2 CHECK THE GENERATOR CURRENT SENSOR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
REPAIR as necessary or INSTALL a new generator current sensor. REFER to Section 414-01 . No GO to H9 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H3 CHECK THE GENERATOR CURRENT SENSOR REFERENCE VOLTAGE CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
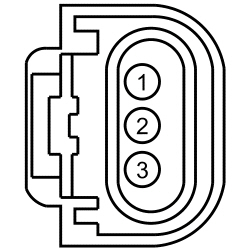 | Yes
GO to H4 . No If the voltage is less than 4.7 volts, REPAIR the circuit for an open or high resistance. If the voltage is greater than 5.1 volts, REPAIR the circuit for a short to voltage. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H4 CHECK THE GENERATOR CURRENT SENSOR SIGNAL RETURN CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to H5 . No REPAIR the circuit for an open or high resistance. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H5 CHECK THE GENERATOR CURRENT SENSOR FEEDBACK CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO GROUND | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to H6 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H6 CHECK THE GENERATOR CURRENT SENSOR FEEDBACK CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
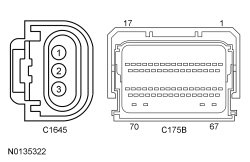
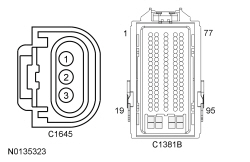 | Yes
GO to H7 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H7 CHECK THE GENERATOR CURRENT SENSOR FEEDBACK CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO VOLTAGE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
REPAIR the circuit. No GO to H8 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H8 CHECK THE GENERATOR CURRENT SENSOR FEEDBACK CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO THE SIGNAL RETURN OR VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to H9 . No REPAIR the affected circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H9 CHECK THE GENERATOR CURRENT SENSOR CONNECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
REPAIR as necessary or INSTALL a new generator current sensor. REFER to Section 414-01 . CLEAR the DTCs. REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, GO to H10 . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by an intermittently loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H10 CHECK FOR CORRECT PCM OPERATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
CHECK OASIS for any applicable TSBs . If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no TSBs address this concern, INSTALL a new PCM. REFER to Section 303-14 . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by module connections. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Pinpoint Test I: DTC U1007:31
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices. Refer to Diagnostic Methods in Section 100-00 for more information.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 13 , Power Distribution/BCM for schematic and connector information.
The battery current sensor is a Hall-effect sensor attached to the battery ground cable. It is supplied a 5 volt reference and ground from the BCM . The BCM reads the battery current sensor feedback voltage to determine how much current is flowing through the battery ground cable.
Before diagnosing or repairing the charging system inspect the following items:
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Lost Communication With Battery Monitoring Sensor "A": No Signal | The BCM does not indicate current from the battery current sensor. |
| Test Step | Result / Action to Take | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
GO to I13 . No GO to I2 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I2 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR REFERENCE VOLTAGE CIRCUIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
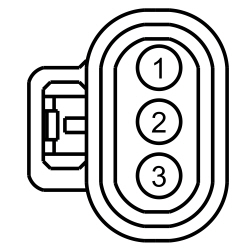 | Yes
GO to I6 . No If the voltage is less than 4.7 volts, GO to I4 . If the voltage is greater than 5.1 volts, GO to I3 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I3 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR REFERENCE VOLTAGE CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO VOLTAGE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
REPAIR the circuit. No REMOVE the fused jumper wire. INSTALL the RUN/START relay and GO to I13 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I4 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR REFERENCE VOLTAGE CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO GROUND | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to I5 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I5 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR REFERENCE VOLTAGE CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
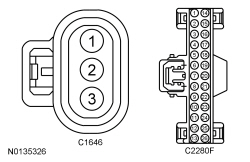 | Yes
GO to I13 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I6 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR SIGNAL RETURN CIRCUIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to I9 . No GO to I7 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I7 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR SIGNAL RETURN CIRCUIT FOR VOLTAGE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
If the voltage is 5.1 volts or less, REPAIR signal return circuit for a short to reference voltage circuit. If the voltage is greater than 5.1 volts, REPAIR signal return circuit for a short to voltage. No GO to I8 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I8 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR SIGNAL RETURN CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to I13 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I9 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR FEEDBACK CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO VOLTAGE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||

 | Yes
REPAIR the circuit. No REMOVE the fused jumper wire. INSTALL the RUN/START relay and GO to I10 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I10 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR FEEDBACK CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO GROUND | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to I11 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I11 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR FEEDBACK CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to I12 . No REPAIR the circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I12 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR FEEDBACK CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO THE SIGNAL RETURN OR REFERENCE CIRCUIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | Yes
GO to I13 . No REPAIR the affected circuit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I13 CHECK THE BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR CONNECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
REPAIR as necessary or INSTALL a new battery current sensor. REFER to Section 414-01 . CLEAR the DTCs. REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, GO to I14 . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I14 CHECK FOR CORRECT BCM OPERATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes
CHECK OASIS for any applicable TSBs . If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no TSBs address this concern, INSTALL a new BCM . REFER to Section 419-10 . No The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by module connections. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |